The Lycoming O-320 is a popular four-cylinder, air-cooled, horizontally opposed piston aircraft engine widely used in a variety of light aircraft. Known for its reliability, durability, and performance, the O-320 series has been a mainstay in general aviation for decades.
History and Development
The Lycoming O-320 series was introduced in the late 1950s as an upgrade from the smaller O-235 and O-290 engines. It was designed to provide more power while maintaining the same level of reliability and ease of maintenance that Lycoming engines were known for.
The O-320 quickly became a preferred choice for many aircraft manufacturers and has been installed in a wide range of aircraft models.
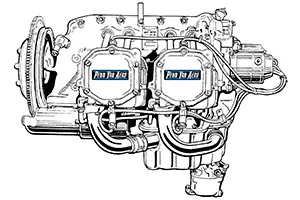
Design and Features
The O-320 is a horizontally opposed, four-cylinder, direct-drive engine. Here are some of its key design features:
- Horizontally Opposed Configuration: This design helps in reducing vibration and providing a compact, aerodynamic profile for installation in light aircraft.
- Air-Cooled: The engine relies on airflow over the cylinders for cooling, eliminating the need for a complex liquid cooling system.
- Direct Drive: The propeller is directly connected to the crankshaft, which simplifies the power transmission mechanism and improves reliability.
- Magneto Ignition: Traditional magneto ignition systems are used for reliable engine starting and operation.
Lycoming O-320 Specifications
Here are the detailed specifications for the Lycoming O-320 engine:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Lycoming Engines |
| First Introduced | Late 1950s |
| Configuration | Horizontally opposed, four-cylinder |
| Displacement | 320 cu in (5.24 L) |
| Bore x Stroke | 5.125 in x 3.875 in (130.2 mm x 98.4 mm) |
| Compression Ratio | 7.00:1 to 8.50:1 (varies by model) |
| Power Output | 150 hp to 160 hp (112 kW to 119 kW) |
| Fuel Type | 100LL avgas |
| Dry Weight | 244 lbs (111 kg) |
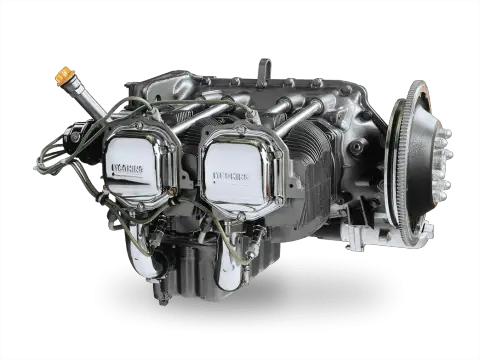
Lycoming O-320 Performance and Variants
The O-320 series has multiple variants, each optimized for different performance characteristics and aircraft applications. Some of the notable variants include:
- O-320-A1A: Produces 150 hp at 2700 RPM, commonly used in a variety of general aviation aircraft.
- O-320-B2B: Produces 160 hp at 2700 RPM, featuring higher compression for improved power output.
- O-320-D2J: Another 160 hp variant, widely used in training aircraft and light utility aircraft.
Applications
The Lycoming O-320 engine is used in a wide range of aircraft, including but not limited to:
- Piper PA-28 Cherokee: A popular training and touring aircraft.
- Cessna 172 Skyhawk: One of the most well-known and widely used training aircraft in the world.
- Piper PA-18 Super Cub: Known for its excellent short takeoff and landing (STOL) capabilities.
- Grumman American AA-5: A light aircraft used for training and personal flying.
- Robinson R22 Helicopter: A light utility and training helicopter.
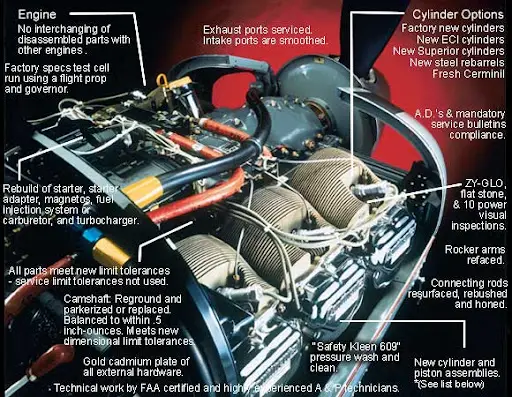
Maintenance and Overhaul
The Lycoming O-320 is known for its straightforward maintenance procedures and durability. Regular maintenance includes inspections, oil changes, and periodic component replacements. The Time Between Overhaul (TBO) for the O-320 is typically around 2,000 hours, although this can vary based on operating conditions and maintenance practices.
Lycoming O-320 Price
The price of a Lycoming O-320 engine can vary widely based on its condition, whether it is new, overhauled, or used, and any additional features or modifications. As of 2024, prices generally range from:
- New Engines: $35,000 to $45,000 – These are factory-new engines with full warranties and the latest design improvements.
- Overhauled Engines: $20,000 to $30,000 – Engines that have been completely disassembled, inspected, and rebuilt to factory specifications.
- Used Engines: $10,000 to $20,000 – These engines are sold as-is and may require significant work to reach airworthy condition.
FAQs
1. What is the Lycoming O-320 engine?
The Lycoming O-320 is a four-cylinder, horizontally opposed, air-cooled aircraft engine designed for light aircraft. It is one of Lycoming’s most popular engine models, offering reliability, efficiency, and moderate power output, typically ranging from 150 to 160 horsepower.
2. What are the specifications of the Lycoming O-320 engine?
Key specifications include:
- Configuration: Horizontally opposed, 4-cylinder
- Displacement: 320 cubic inches (5.24 liters)
- Horsepower: 150-160 HP, depending on the variant
- Weight: ~244 lbs (dry weight)
- Fuel Consumption: 8-10 gallons per hour (GPH)
- Compression Ratio: 7.00:1 to 8.50:1, depending on the model
3. Which aircraft commonly use the Lycoming O-320?
The O-320 is widely used in a variety of light aircraft, including:
- Cessna 172 Skyhawk
- Piper PA-28 Cherokee
- Piper PA-18 Super Cub
- Robinson R22 Helicopter (modified variants)
- Many experimental and homebuilt aircraft
4. What fuel does the Lycoming O-320 use?
The Lycoming O-320 typically runs on aviation gasoline (avgas), with most models using 100LL fuel. Some models are approved for unleaded mogas (automotive gasoline) when certified under an FAA Supplemental Type Certificate (STC).
5. How much does a Lycoming O-320 engine cost?
Prices for a Lycoming O-320 engine depend on its condition and type:
- New engine: $30,000 to $50,000
- Overhauled engine: $15,000 to $25,000
- Used engine: $10,000 to $20,000 (depending on hours and condition)
6. What is the Time Between Overhaul (TBO) for the Lycoming O-320?
The TBO for a Lycoming O-320 engine is typically between 2,000 and 2,400 flight hours, depending on the specific model and operating conditions.
7. What are the variants of the Lycoming O-320 engine?
The O-320 has several variants, including:
- O-320-A, B, C, and D: Differing in horsepower and compression ratios.
- IO-320: Fuel-injected version.
- HIO-320: Helicopter-specific variant.
- AEIO-320: Aerobatic variant, designed for inverted flight.
8. Can the Lycoming O-320 be used in experimental aircraft?
Yes, the O-320 is a popular choice for experimental and homebuilt aircraft due to its affordability, reliability, and wide availability. Many builders use overhauled or surplus O-320 engines to power their projects.
9. What are the advantages of the Lycoming O-320?
- Reliability: Proven track record over decades of operation.
- Versatility: Fits a wide range of aircraft and applications.
- Fuel efficiency: Reasonable consumption for its power class.
- Ease of maintenance: Widely supported by service manuals, parts suppliers, and mechanics.
10. What are common issues with the Lycoming O-320?
While generally reliable, common issues include:
- Cylinder wear: Especially in high-use engines.
- Carburetor icing: In carbureted models under certain weather conditions.
- Oil leaks: Often due to aging gaskets or seals.
- Magneto failure: Requires regular inspections and servicing.
11. How does the Lycoming O-320 compare to the O-360?
- Power: The O-360 has a larger displacement (360 cubic inches) and produces 180-200 HP, compared to the O-320’s 150-160 HP.
- Weight: The O-320 is lighter, making it a better choice for smaller aircraft.
- Cost: The O-320 is generally more affordable to purchase and maintain.
12. Can the Lycoming O-320 be upgraded?
Yes, there are several upgrades available for the O-320, including:
- High-compression pistons: To increase horsepower.
- Electronic ignition systems: For improved reliability and fuel efficiency.
- STCs for mogas: To allow the use of automotive gasoline.
13. What is the typical maintenance schedule for the Lycoming O-320?
Regular maintenance includes:
- Oil changes: Every 25-50 flight hours or as recommended.
- Magneto inspections: Every 500 hours.
- Compression checks: During annual inspections.
- Spark plug replacement: Based on wear and engine performance.
14. How does the Lycoming O-320 perform in different climates?
The O-320 is highly adaptable and performs well in a variety of climates. However, pilots operating in cold weather should use pre-heating equipment to avoid cold starts, and those in humid climates should take measures to prevent corrosion.
15. Where can I find parts for the Lycoming O-320?
Parts for the Lycoming O-320 are widely available from:
- Authorized Lycoming dealers.
- Aviation parts suppliers like Aircraft Spruce and Wicks Aircraft.
- Salvage yards and aviation forums for used or rare components.
16. Is the Lycoming O-320 fuel-efficient?
The Lycoming O-320 is considered fuel-efficient for its power class, with a consumption rate of 8-10 gallons per hour at cruise settings. Adjusting power settings and leaning the mixture can optimize fuel usage further.
17. What is the history of the Lycoming O-320 engine?
The O-320 was introduced in the 1950s as an evolution of Lycoming’s smaller engines, aiming to provide more power for light aircraft. Its design has remained largely unchanged due to its effectiveness and reliability, making it a staple in general aviation.
18. Are there modern alternatives to the Lycoming O-320?
Modern alternatives include engines like:
- Continental IO-240 or IO-360 (fuel-injected options).
- Rotax 915iS (for experimental and light-sport aircraft).
- Diesel-powered engines for those seeking alternative fuel sources.




Leave a comment