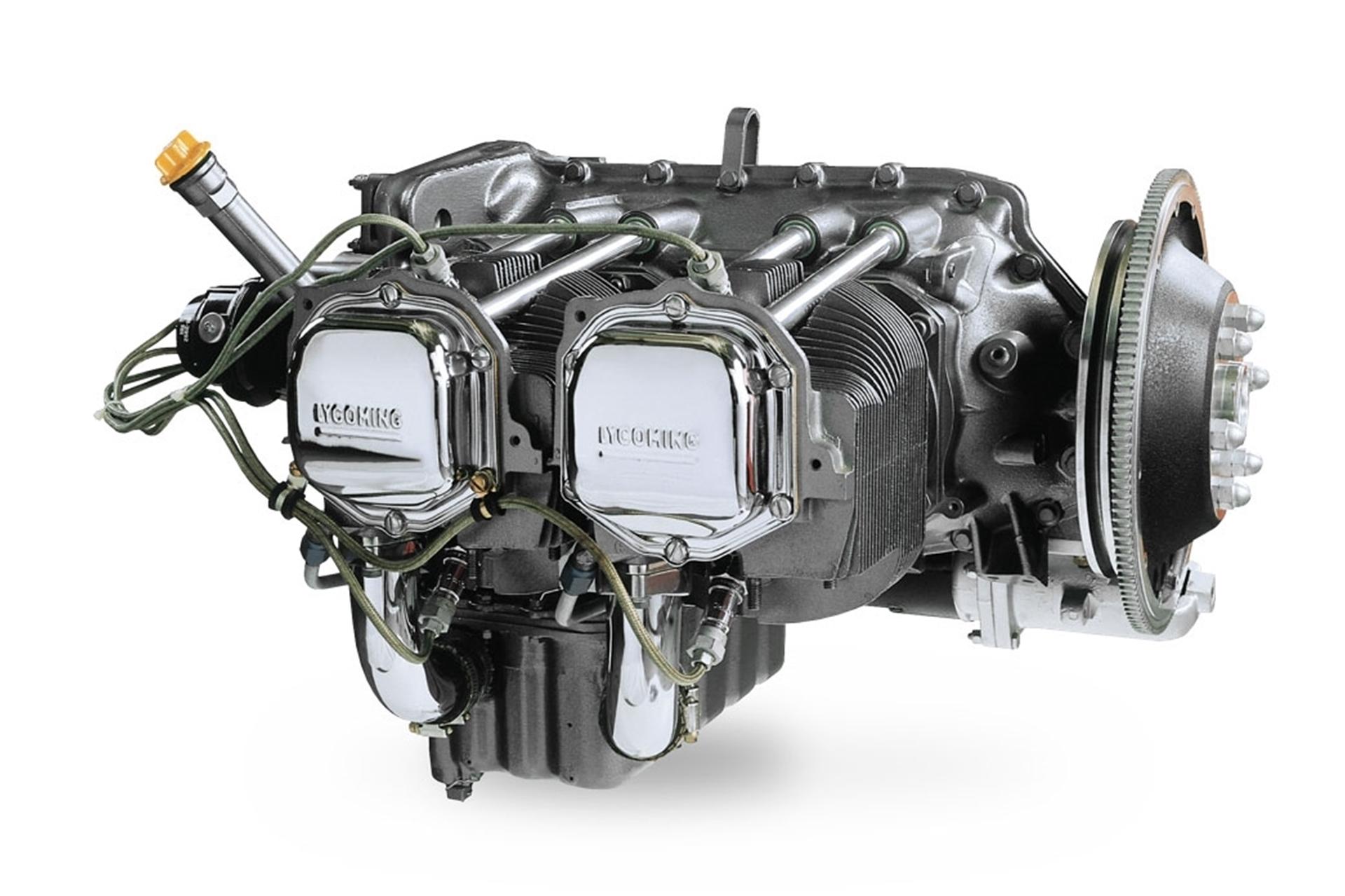
Lycoming O-235 is a family of four-cylinder, air-cooled, horizontally opposed piston engines designed for light aircraft. Renowned for its reliability, simplicity, and ease of maintenance, the O-235 series has been a popular choice for general aviation aircraft for decades. This article provides an in-depth look at the specifications, performance, applications, and legacy of the Lycoming O-235 engine.
Specifications of the Lycoming O-235
Here are the key specifications of the Lycoming O-235 engine:
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Configuration | Horizontally opposed 4-cylinder |
| Displacement | 233.3 cubic inches (3.82 liters) |
| Bore | 4.375 inches (111.1 mm) |
| Stroke | 3.875 inches (98.4 mm) |
| Compression Ratio | 6.75:1 to 9.7:1 |
| Power Output | 100 hp (75 kW) to 125 hp (93 kW) |
| Fuel System | Carbureted or Fuel Injected |
| Cooling System | Air-cooled |
| Ignition System | Magneto-based |
| Dry Weight | Approximately 244 lbs (111 kg) |
| Fuel Type | 100LL Aviation Gasoline (AvGas) |
| Oil Capacity | 6 quarts (5.7 liters) |

Lycoming O-235 Performance
The Lycoming O-235 offers a range of performance characteristics that make it suitable for light aircraft:
- Reliability: Known for its robust construction and dependability, the O-235 has a long service life with proper maintenance.
- Efficiency: The engine’s design provides a good balance of power and fuel efficiency, making it economical for general aviation use.
- Ease of Maintenance: The simple design and widespread availability of parts make the O-235 easy to maintain and service.
- Versatility: The O-235 series includes various models with different power outputs and features, catering to a wide range of aircraft.
Lycoming O-235 Variants
The Lycoming O-235 series includes several variants, each with specific features and improvements:
- O-235-C1: One of the earliest models, producing 115 horsepower.
- O-235-L2C: A popular variant used in training aircraft, producing 115 horsepower.
- O-235-N2C: Known for its improved fuel efficiency and producing 118 horsepower.
- O-235-F1: A higher compression version, producing up to 125 horsepower.

Lycoming O-235 Applications
The Lycoming O-235 engine is used in a wide variety of light aircraft, including:
- Piper PA-18 Super Cub: A well-known light aircraft used for training, recreation, and bush flying.
- Cessna 152: A popular training aircraft used by flight schools worldwide.
- Grumman American AA-1: A light aircraft used for recreational flying.
- Piper PA-28-140 Cherokee: A common aircraft for training and personal use.
- Aeronca 15AC Sedan: An aircraft used for training and recreational flying.
Maintenance and Operation
For aircraft owners and operators, the Lycoming O-235 is known for its straightforward maintenance requirements:
- Regular Inspections: Routine inspections and adherence to maintenance schedules are essential to ensure longevity and reliability.
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes are crucial to maintain engine health and performance.
- Magneto Checks: Periodic checks and maintenance of the magneto ignition system are necessary to ensure proper operation.
- Overhaul Intervals: The O-235 typically requires an overhaul after 2,000 hours of operation, though this can vary based on usage and operating conditions.

Lycoming O-235 Price
Price Ranges
New Engines:
Price Range: $25,000 to $35,000
Description: Brand new Lycoming O-235 engines are rare and typically very expensive due to the manufacturing costs and modern enhancements that may be included. Prices can vary based on the specific model and configuration.
Overhauled Engines:
Price Range: $15,000 to $25,000
Description: Overhauled engines have been completely disassembled, inspected, and rebuilt with new or refurbished parts to restore them to a like-new condition. The cost depends on the quality of the overhaul, the reputation of the overhaul facility, and any warranties provided.
Used Engines:
Price Range: $8,000 to $15,000
Description: Used Lycoming O-235 engines in good, running condition can be found within this price range. These engines may have higher flight hours and might require some maintenance but are generally airworthy and functional.
Core Engines (For Rebuild):
Price Range: $3,000 to $8,000
Description: Core engines are typically sold as-is for the purpose of being overhauled. These engines are not airworthy in their current state and will need significant work to become operational. This option is suitable for those looking to perform their own rebuild or have it done by a specialist.
FAQs
1. What is the Lycoming O-235 Engine?
The Lycoming O-235 is a four-cylinder, air-cooled, horizontally opposed piston engine. It is widely used in light aircraft due to its reliability, efficiency, and ease of maintenance.
2. What aircraft use the Lycoming O-235 engine?
The O-235 engine is commonly found in light aircraft, including:
- Cessna 152
- Piper PA-18-150 Super Cub (specific variants)
- Diamond DA20 Katana
- Aeronca Champion (some models)
- Various experimental and homebuilt aircraft.
3. What are the specifications of the Lycoming O-235 engine?
Typical specifications include:
- Configuration: Horizontally opposed, 4-cylinder.
- Displacement: 233.3 cubic inches.
- Horsepower: 108-125 HP, depending on the variant.
- Compression Ratio: 6.75:1 to 8.5:1, depending on the model.
- Weight: ~250 lbs (dry).
- Fuel Type: 100LL (low-lead) avgas.
4. How many variants of the Lycoming O-235 engine are there?
There are several variants of the O-235, including:
- O-235-C series: Early models producing ~108 HP.
- O-235-L series: Higher compression models with ~118 HP.
- O-235-N2C: Used in the Cessna 152, producing 110 HP.
- O-235-F series: Modified versions with carburetor or fuel-injection systems for better efficiency.
5. What makes the Lycoming O-235 engine reliable?
The O-235 engine’s reliability stems from its:
- Simple design: Fewer moving parts reduce the likelihood of failure.
- Air-cooled construction: Eliminates the complexity of liquid cooling systems.
- Proven track record: Used in thousands of aircraft for decades.
6. What is the TBO (Time Between Overhaul) for the Lycoming O-235 engine?
The typical TBO for the Lycoming O-235 engine ranges between 2,000 and 2,400 hours, depending on the specific variant and operating conditions.
7. What fuel does the Lycoming O-235 engine use?
The O-235 engine typically uses 100LL avgas. However, some variants can operate on unleaded avgas or mogas, depending on specific modifications and approvals.
8. What oil is recommended for the Lycoming O-235 engine?
Lycoming recommends using aviation-grade oils:
- Ashless dispersant oils: For most operating conditions.
- Straight mineral oil: During the engine break-in period.
9. How does the Lycoming O-235 engine compare to similar engines?
Compared to competitors like the Continental O-200:
- The O-235 offers higher horsepower (118-125 HP vs. 100 HP).
- It is slightly heavier but delivers better performance in many applications.
- It has a longer service history and broader parts availability.
10. What is the fuel efficiency of the Lycoming O-235 engine?
The O-235 engine is known for its fuel efficiency, consuming approximately 6-8 gallons per hour in cruise settings, depending on the aircraft and power settings.
11. Can the Lycoming O-235 engine run on unleaded fuel?
Some O-235 variants have been approved to run on unleaded avgas or mogas with the appropriate STC (Supplemental Type Certificate). Check with your manufacturer or engine manual for compatibility.
12. Is the Lycoming O-235 engine suitable for aerobatic aircraft?
While the O-235 is not specifically designed for aerobatic use, some models, like the Pitts Special, have used similar engines. For sustained aerobatic operations, modifications may be necessary.
13. How much does a Lycoming O-235 engine cost?
The cost of a new or overhauled Lycoming O-235 engine typically ranges from $20,000 to $35,000, depending on the variant and condition.
14. What are common maintenance tasks for the Lycoming O-235 engine?
Key maintenance tasks include:
- Oil changes: Every 25-50 flight hours or as specified.
- Spark plug checks: Clean and replace as needed.
- Valve inspections: To ensure proper seating and operation.
- Magneto timing: Verify and adjust regularly.
- Air filter replacements: To maintain optimal airflow.
15. Are there modern upgrades available for the Lycoming O-235 engine?
Yes, upgrades include:
- Electronic ignition systems: For improved efficiency and reliability.
- Lightweight starters and alternators: To reduce overall weight.
- Fuel injection kits: For better fuel economy and performance.
16. What are the common issues with the Lycoming O-235 engine?
While the O-235 is highly reliable, common issues include:
- Lead fouling: Due to 100LL avgas.
- Exhaust valve wear: Particularly in high-use engines.
- Carburetor icing: In certain weather conditions, especially with carbureted models.
17. How long has the Lycoming O-235 engine been in production?
The Lycoming O-235 engine was introduced in the 1940s and has remained in production for over 70 years, making it one of the most enduring engines in aviation history.
18. What certifications are required to install a Lycoming O-235 engine?
The O-235 engine requires FAA certification for installation in certified aircraft. Experimental aircraft can install it with fewer regulatory requirements but should follow manufacturer guidelines.
19. Can the Lycoming O-235 engine be overhauled?
Yes, the O-235 can be overhauled to extend its service life. Overhaul costs range from $12,000 to $18,000, depending on the scope of work and parts needed.
20. Why is the Lycoming O-235 engine still popular today?
The O-235 remains popular due to its:
- Proven reliability and performance.
- Widespread availability of parts and support.
- Versatility: Used in training aircraft, recreational planes, and even experimental builds.


Leave a Reply