Instrument Landing System (ILS) and Microwave Landing System (MLS) are both vital tools used in aviation for precision approach and landing guidance. While they serve similar purposes, there are distinct differences between the two systems. Let’s delve into the dissimilarities and unique features of ILS and MLS.
Instrument Landing System (ILS)
ILS is a ground-based navigation aid that provides precise guidance to aircraft during approach and landing in adverse weather conditions or low visibility. It consists of two main components:
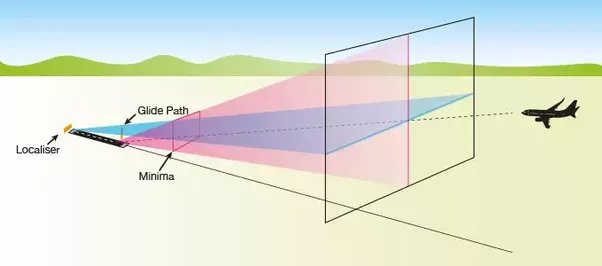
- Localizer (LLZ): The localizer provides lateral guidance, ensuring the aircraft remains aligned with the centerline of the runway. It emits signals along the extended centerline of the runway, allowing pilots to make course corrections for alignment.
- Glide Slope (GS): The glide slope provides vertical guidance, assisting pilots in maintaining the correct descent path towards the runway. It emits signals at a specific angle, indicating the proper rate of descent for a safe landing.
ILS operates in the VHF (Very High Frequency) band and is widely used in airports worldwide for its accuracy and reliability.
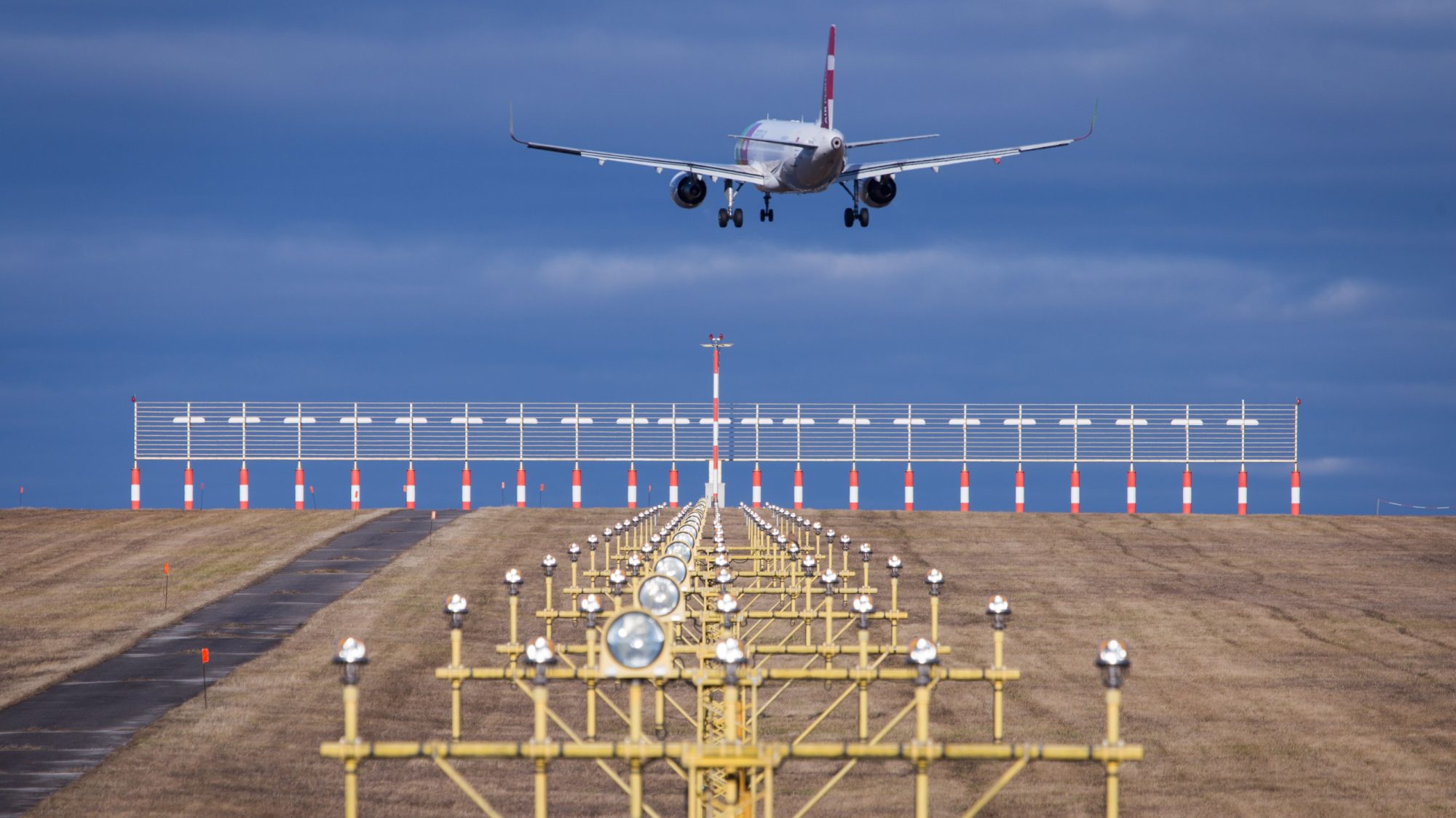

Microwave Landing System (MLS)
MLS is an advanced landing system that utilizes microwave signals for precision approach and landing guidance. Unlike ILS, MLS offers several additional features and capabilities:
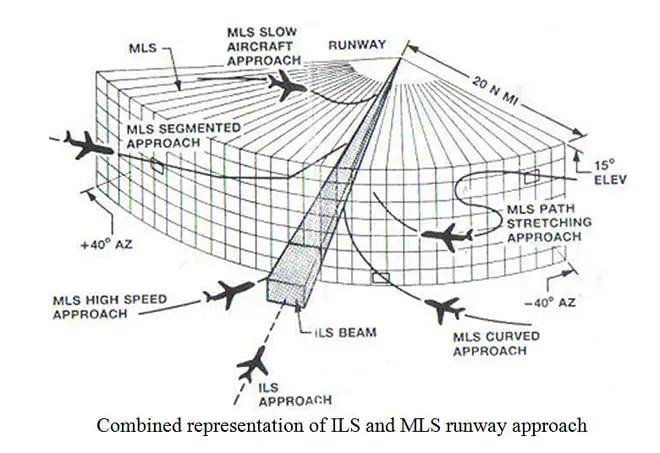
- Flexibility: MLS provides greater flexibility in establishing approach paths and can accommodate curved or segmented approaches, offering more options for runway access in complex airport layouts.
- Precision: MLS offers higher accuracy and resolution compared to ILS, particularly in challenging terrain or congested airspace environments.
- Multiple Runway Access: MLS can serve multiple runways simultaneously, providing independent approach paths for each runway without interference.
- Reduced Signal Interference: MLS operates in the microwave frequency band, which is less susceptible to interference from ground clutter, terrain, or other aircraft, enhancing reliability and performance.
Differences Between ILS and MLS
- Technology: ILS relies on VHF signals, while MLS utilizes microwave signals, offering different levels of accuracy and performance.
- Flexibility: MLS provides greater flexibility in establishing approach paths and accommodating diverse airport configurations compared to ILS.
- Precision: MLS offers higher precision and resolution, particularly in challenging environments where accurate guidance is critical for safe landings.
- Interference: MLS is less susceptible to signal interference from ground clutter or other sources compared to ILS, enhancing reliability and performance.
If you are interested you should read about Pitot & Static Blockage
ILS and MLS advantages & disadvantages
here’s a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of both Instrument Landing System (ILS) and Microwave Landing System (MLS):
| Aspect | ILS | MLS |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | – Widely implemented and standardized worldwide | – Offers greater flexibility in approach paths |
| – Provides reliable guidance in adverse weather | – Higher precision and resolution | |
| – Well-established infrastructure at many airports | – Accommodates multiple runways simultaneously | |
| – Lower installation and maintenance costs | – Less susceptible to signal interference | |
| – Suitable for most airport configurations | – Reduced reliance on ground-based infrastructure | |
| Disadvantages | – Limited flexibility in approach paths | – Higher initial installation costs |
| – Lower precision and resolution compared to MLS | – Requires additional training for pilots and ATC | |
| – Susceptible to signal interference and ground clutter | – Limited availability and adoption at some airports | |
| – May experience disruptions during maintenance | – Potential for electromagnetic interference | |
| – Less accurate in complex airspace environments | – Integration challenges with existing systems |
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of both ILS and MLS can help aviation professionals make informed decisions regarding approach and landing procedures, considering factors such as airport layout, weather conditions, and system reliability.


Leave a comment